通过一个Flink排查异常,深究一下flink state
- 3 mins背景
事件起因是一个朋友使用flink 状态的时候遇到了一个报错,同时提供了相关代码,找我帮忙看下。  主要的具体报错信息如下:
主要的具体报错信息如下:
IllegalArgumentException: key group 99 is not in KeyGroupRange{starKey=90, endKeyGroup=95}. Unless you`re directly using low level state access APIs,
这个算是flink keyed state中比较典型的错误了,正好通过这个flink 异常的排查过程,和大家一起深究下FLink state 的基础原理。
Flink State
官方文章:A Deep Dive into Rescalable State in Apache Flink
官方把state 分为两种 Operator state 和 Keyed state ,具体解释如下:
For Flink’s stateful stream processing, we differentiate between two different types of state: operator state and keyed state. Operator state is scoped per parallel instance of an operator (sub-task), and keyed state can be thought of as “operator state that has been partitioned, or sharded, with exactly one state-partition per key”. We could have easily implemented our previous example as operator state: all events that are routed through the operator instance can influence its value.
官方的图片,上面的是无状态的flink 任务扩缩容,下图是有状态flink 任务,checkpoint的时候,会将状态 snapshot到外置分布式存储系统中(rocksdb, s3, hdfs 等),同时扩缩容的时候,需要考虑相关状态如何分发。
Operator state
官方这里举的例子是 flink kafka consumer 状态,记录了小的kafka topic 以及相关offset,在扩缩容的时候,需要在相关task分配具体状态。
这里的图片有一定误导,我第一次读到这里,会有一个疑问,就是ListCheckpointed 如何做到每个task 读取只属于自己的那部分状态?其实并没有,每个task 读取全量数据,至于使用哪部分数据,是kafka consumer 内部自己根据task index 自行做了判断。无图无真相,在FlinkKafkaConsumerBase的初始化方法
public void open(Configuration configuration) throws Exception 中有这么一段代码如下:
for (Map.Entry<KafkaTopicPartition, Long> restoredStateEntry :
restoredState.entrySet()) {
// seed the partition discoverer with the union state while filtering out
// restored partitions that should not be subscribed by this subtask
if (KafkaTopicPartitionAssigner.assign(
restoredStateEntry.getKey(),
getRuntimeContext().getNumberOfParallelSubtasks())
== getRuntimeContext().getIndexOfThisSubtask()) {
subscribedPartitionsToStartOffsets.put(
restoredStateEntry.getKey(), restoredStateEntry.getValue());
}
}
可以看到 assign 方法中决定了当前的topic 是否订阅消费, assign方法内部主要原理是实现了一个round-robin 方法,来负载订阅,代码如下: ```java public class KafkaTopicPartitionAssigner { public static int assign(KafkaTopicPartition partition, int numParallelSubtasks) { int startIndex = ((partition.getTopic().hashCode() * 31) & 0x7FFFFFFF) % numParallelSubtasks; // here, the assumption is that the id of Kafka partitions are always ascending // starting from 0, and therefore can be used directly as the offset clockwise from the // start index return (startIndex + partition.getPartition()) % numParallelSubtasks; } }
到这里可以比较清晰了解到,每个task 获取ListCheckponited 的状态依旧是全量,只是在调用open方法的时候,会根据自身的indexOfThiSubtask 来判断使用哪部分数据。
#### Keyed state
和上面不同,keyBy 之后的状态只是读取task 所属的部分状态,但是还引入了另外一个问题,如果单纯的使用hask(key)%parallelism 的方式来决定每个task 取哪部分数据,会导致随机读取数据,无法实现**顺序读写**的性能优势,这在状态很大的场景下,是很有性能劣势的。
所以flink 官方引入了一个key group 的概念,具体算法也如图上所示,可以同时兼顾顺序读取数据。

### 排错
好了,基本的state状态的机制我们大致了解了一下,回到具体的报错信息,如图:
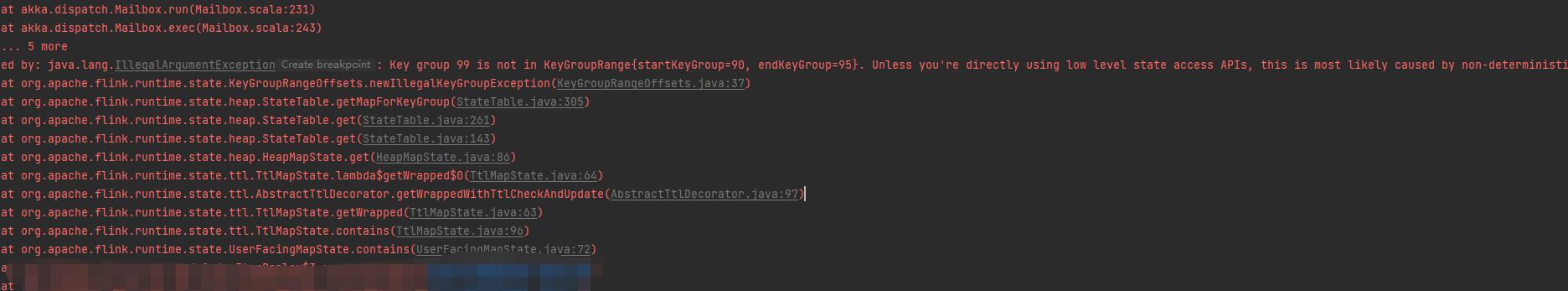
主要的具体报错信息如下:
IllegalArgumentException: key group 99 is not in KeyGroupRange{starKey=90, endKeyGroup=95}. Unless you`re directly using low level state access APIs,
这次可以比较清晰的理解了,具体报错原因,就是使用的key 值通过hash 之后计算的key_group不在当前的task 所属的key group 范围。
由此可以猜测对key 进行hash 之后不是一个**稳定的值**, 我们看下官方具体计算key group的方法:
```java
// org.apache.flink.runtime.state.KeyGroupRangeAssignment#assignToKeyGroup
/**
* Assigns the given key to a key-group index.
*
* @param key the key to assign
* @param maxParallelism the maximum supported parallelism, aka the number of key-groups.
* @return the key-group to which the given key is assigned
*/
public static int assignToKeyGroup(Object key, int maxParallelism) {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(key, "Assigned key must not be null!");
return computeKeyGroupForKeyHash(key.hashCode(), maxParallelism);
}
可以看到具体的hash 方法使用的是对象本身的hashCode()方法,number_of_key_group使用的是maxParallelism 配置。现在基本已经破案了,我们只需要去看下提供的代码里key的设置,是不是哪里存在问题。
最后朋友写的源码就不放上来了,可以描述下,他的实现中使用到了Joiner 来将多个字段拼接,然后作为key值,本身这个逻辑是没问题的,但是他写的时候忘记了Joiner.toString(),而是直接传了Joiner对象,因为Object.hashCode本身的值也是根据对象内存地址来计算的,这样就导致了没有使用string的hascode方法,而是使用的object的原始方法,导致hash值不稳定。
总结
flink 状态官方分为两种,operator state 和 keyed state 两种, keyed state 中内部设计了 key group 概念,根据定义个key的hashcode 和 设置的maxParallelism值(这里注意,后续如果手动改变maxParallelism 值,会导致基于savepoint 启动异常)计算出具体的所属key group ,key group 的设计为了每个task 在扩缩容的情况下 ,依旧拥有顺序读取状态的能力。
好了 今天就告一段落,我们下期再见~~~
参考资料
# Flink状态的缩放(rescale)与键组(Key Group)设计
# FLINK-18637 Key group is not in KeyGroupRange
# A Deep Dive into Rescalable State in Apache Flink
# Flink 源码阅读笔记(10)- State 管理